The year 2020 has seen unprecedented uncertainty and upheaval. In the midst of it all, we have seen various technology trends that drove 2020 and are set to make an impact on the business landscape in 2021. To grow businesses in 2021, it’s imperative to adopt technology that complements and enables the overarching business strategy. Leaders must continuously stay abreast of the emerging technology trends on the horizon. This will help business leaders to build integrated corporate strategies and take calculated risks that have a high probability of paying off in 2021.
In this blog, we’ll review the top tech trends of 2020 and how they will manifest in 2021. We’ll also take a look at some tech trends of 2021 that the world can look forward to.
Engineering Strategy
2020 Recap: The role of technology in business strategy has never been more critical. With technology disrupting all areas of business, 2020 proved that it is more critical than ever to have technology inform business decisions. If formulated and executed correctly, this enables companies to have a more agile and nimble approach to corporate strategy. As technology advances at a pace more rapid than ever before, 2020 showed that these changes will need to be brought about quickly. For example, tech strategy can be constrained by corporate strategy. In such a scenario, because corporate strategy is considered to be of greater importance, technological development or adoption can fall by the wayside. To avoid this, it’s necessary for corporate and technology strategy to go hand in hand, and for corporate technology leaders to feel empowered to make such decisions.
2021 Outlook: In a Deloitte survey, 40% of CEOs believed that the CIO would be the driver of business strategy. This is clear evidence that as strategy and technology become inextricably intertwined, technology must inform strategic intentions and vice versa. To do this, many decision makers are investing in tech-enabled strategy. This means that not only are the corporate strategies themselves becoming informed by technology, but the process of developing, executing, and monitoring strategies is also becoming more technologically-enabled. This means leveraging tech-enabled strategy platforms and tools that allow decision makers to think about a wider range of variables. These include futuristic trend-sensing technologies that scan the environment to collect and analyze factors that have an impact on overall strategy. This includes changes in the external environment, such as transforming social, legal, and political regulations. Changes in the industry, customer expectations, and stakeholder thought process will also be considered. Other types of technology helps leaders to simulate and test the results of choosing a particular strategic path to manage critical uncertainties. This helps to create alternate scenarios to identify and mitigate risks and threats. Finally, monitoring and analytics tools track outcomes to inform current and future strategic discussions about the organization’s performance against the defined strategy. With these tools, stakeholders can assess the strategy’s impact, what is working well, and what needs to be changed. In 2021, all this will be done while pursuing alliances and ecosystem partnerships with leading organizations. As the world becomes more collaborative and hyperconnected, these alliances will go a long way in maintaining a unique competitive advantage.
The Digitalization Wave
2020 Recap: The pandemic has reiterated the need for every business to become a digital business. With most business operations being carried out remotely in the interests of social distancing, the need for organizations to have policies, practices, and technology for this to become feasible intensified. As part of this, businesses had to adopt agile practices, reskill, and retool to keep up with the wave of digitalization that had begun before the pandemic and had accelerated during the months of lockdown. After all, in the era of digitalization, what is more important than the size of an organization is how quickly it responds and adapts to constantly changing conditions.
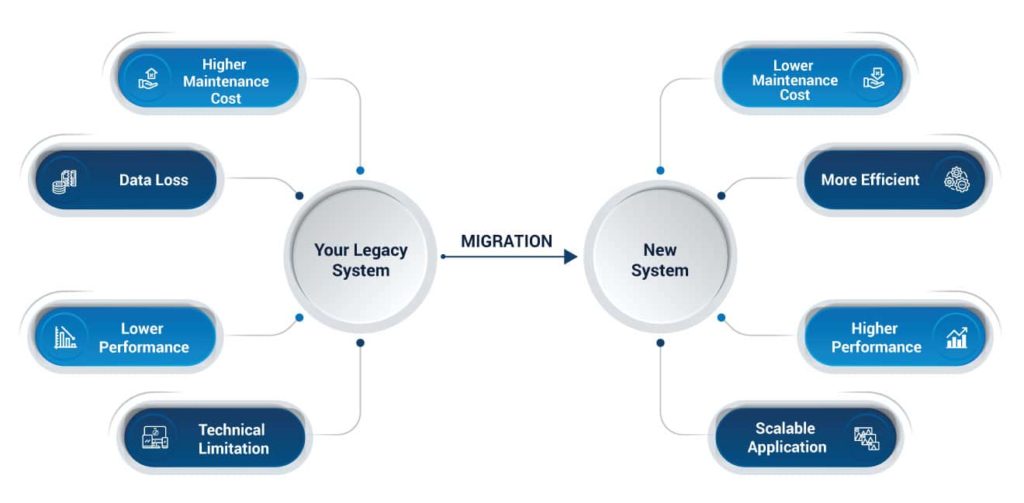
2021 Outlook: One important aspect of digitalization is reviving or revitalizing the core of technology operations in the organization. This includes breathing new life into legacy systems with a new generation of powerful, easy to use, low-code platforms. This means that in 2021, organizations will have to think about reducing technical debt by refactoring or re-architecting critical applications. One important way of reducing legacy system debt is to consider migrating critical IT assets, in addition to data and workloads, to the cloud. Whether the organization decides to use a lift-and-shift approach or re-architect from scratch, moving legacy assets to the cloud will allow you to leverage the benefits of scalability, agility, and cost-effectiveness of a cloud-first model, whether the organization decides to select a single cloud, multi-cloud, or hybrid cloud strategy.
Upgrading entire legacy systems, for example ERP systems, can seem complicated, time-consuming, and expensive due to various factors such as outdated governance requirements, spaghetti code, and dated workarounds and fixes. In such a case, migrating to the cloud or undertaking other modernization initiatives will have a significant time and money cost. To circumvent this, technology can enable this to be streamlined, for example by using sophisticated algorithms to understand which area of an ERP system will have the most significant impact on the bottom line. Using tools, you can even recode critical applications (leaving your existing ERP system intact) or replatform them in ways that minimize technical debt. The crux of the matter is that applications and legacy systems should be modernized so that they add value to your business instead of being a liability to it. With tightening budgets in the midst of a slowed economy, the pressure will be on for organizations to make the most use of their existing assets. Because of this, the digitalization wave is set to gain momentum in 2021.
MLOps
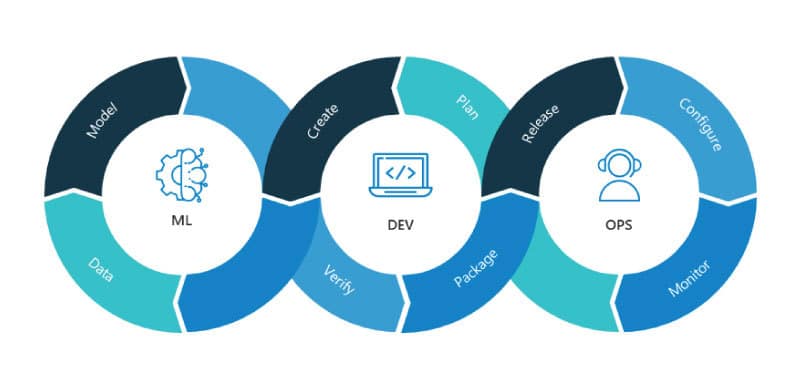
2020 Recap: MLOps is a concept similar to DevOps; indeed, delivery management problems were a key driver behind the emergence of DevOps two decades ago. As of 2020, ML model delivery continued to be slow – a survey by Deloitte found that 22% of business decision makers state that it takes between 1 and 3 months to deploy a machine learning model into production, while it takes more than 3 months for 18% of business decision makers. Additionally, there is a lack of expertise, production-ready data, and integrated development environments. Another problem is that ML models are created by a handful of experts. Although these models are clever, scalability and consistent deployment are issues. All of these reasons are why forward-thinking organizations have started to apply DevOps principles to implement Machine Learning Operations, or MLOps.
2021 Outlook: By standardizing and automating ML model development, deployment, and management, organizations will be able accelerate the delivery schedule while maintaining quality and efficiency. MLOps will provide business value as a result of this automation by improving the quality and speed at which the ML models are deployed. By monitoring key metrics, organizations will be further able to optimize their ML model development.
Just like DevOps, MLOps features automated pipelines, processes, shorter development cycles, and improved collaboration among teams. It also borrows the concepts of continuous testing, deployment, deployment, and monitoring. Because of these, MLOps enables faster development and deployment of ML models as well as more efficient model maintenance. Finally, the data itself that ML models feed on will be largely unstructured and stored mainly on the cloud, in time series databases, and graph databases. Organizations will have to work on removing the implicit bias that is inherent in ML models. In 2021, ethical AI and ML will come to the fore in order to remove the bias the developers unintentionally code into their software. We will also see major strides in explainable AI-ML, which is software that lets human users understand why and how an ML model has arrived at a certain decision. In a related vein, automated feature engineering seems to be an advancement that we can look forward to in 2021.
Zero Trust Architectures & AI in Cybersecurity
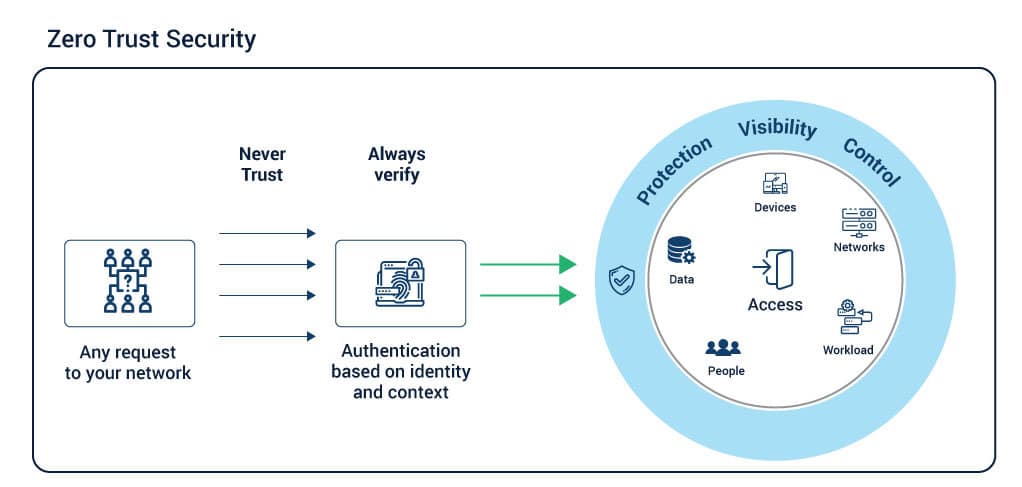
2020 Recap: Increasing digitalization and use of new technologies also means that heightened cybersecurity must be implemented. The ubiquity of tech, a hyperconnected culture, and the growth of 5G, edge computing, and smart devices means that conventional castle-and-moat approaches may not work. With infrastructure and data at times being managed by third-party vendors, the cyber attack surface has expanded. Moreover, with the advancement of AI, algorithms and powerful ML models are redefining the way cybersecurity is handled.
2021 Outlook: This is why zero trust architectures are set to gain wide acceptance. In the traditional model, the trustworthiness of every device and user connected to a network is assumed. In the zero trust architecture, every device and user is authenticated before allowing a connection. Properly designed zero trust architectures embed automation and component orchestration. They can work with other automated practices such as DevSecOps and NoOps. APIs, when used appropriately, can provide a consistent control layer. By using the security services provided by cloud vendors, you can leverage their expertise and continual security investments. Finally, microsegmenting networks, data, applications, and other resources will help you contain any breaches at the least threatening level. By implementing a simplified security technology stack, you can leverage existing systems and tools via API connections to SOAR platforms (security orchestration, automation, and response). This will help automate workflows, coordinate data flows, ensure data security, and auto-remediate known security threats and vulnerabilities. To embed zero-trust principles, organizations will need a philosophical and cultural shift in their approach to cybersecurity.
Another important consideration for cybersecurity in 2021 is AI, and how hackers’ algorithms are pitted against companies’ algorithms to transform the field of cybersecurity. Cybercrime is shifting towards new trends like crypto jacking and ransomware, and hackers can capture data from a variety of sources to publish information on the dark web. AI will expand the cybersecurity landscape to make better cybercrime prediction, auto-remediate attacks, as well as thwart and remove attacks using algorithms. Analytics strategy will enable wider and deeper security insights while exploring new avenues of defense. The AI, in turn, can also create better systems to actively scout for vulnerabilities. Organizations will be able to maintain a steady resource stream of AI-enabled products that will continue to perform the role of cybersecurity threat detection. Because the ML models learn over time, the security approaches will get more sophisticated and controlled. 2021 will see enhancements in the scope of AI in cybersecurity. 2021 will also see the evolution and implementation of various cybersecurity frameworks and SOCs, especially in industries like healthcare where data privacy is critical. Approaches to cloud-native security will also become more sophisticated. In 2021, the discrimination among indicators, anomalies, and behaviors will become finer and more likely to drive business value.
The Digital Workplace
2020 Recap: The Covid-19 pandemic has forced the largest work-from-home experiment. With most employees logging in from home or from a non-traditional work environment, the office rapidly transitioned to a hub for meeting, collaboration, and innovation rather than the traditional venue of work. Some people think that work is forever changed due to the pandemic; although a vaccine is in sight, it will take time until the masses are vaccinated and offices can open without worrying about the virus.
2021 Outlook: Work-from-home is set to continue in 2021. To facilitate this mass, long-term work-from-home situation, organizations need to take certain measures in 2021. If organizations haven’t already, migrating to the cloud has become a need for survival rather than a bonus in the digital workplace. Hybrid and multi cloud environments support secure access and scale according to varying workloads. Cybersecurity and a zero-trust architecture goes hand-in-hand with the move to the cloud. By automating infrastructure and ensuring the virtual availability of all assets, the attack surface for cybercriminals has expanded. To manage this, it is necessary to build zero-trust architectures keeping in mind the points discussed above.
Contrary to popular belief, the digital workplace can be measured, and therefore managed. In 2021, various tools will come to the fore for measuring employee performance and productivity. It will also be easier to keep a pulse on employee morale with the help of digital surveys and data such as boredom, stress, and fatigue levels. Data on these points will help managers to allocate appropriate tasks and ensure that employees avoid burnout. The office may have changed forever, but it is clear that work goes on well remotely and will be improved using technology.
Fog Computing
2020 Recap: As discussed, the cloud is no more a bonus for giving organizations an edge, it is a requirement to survive in the digital-first world of the future. 2020 brought the concept of fog computing to the fore; this is one step beyond fog computing. A problem with cloud computing is the potential of latency due to data being sent to the cloud for analysis. Fog computing solves this problem by analyzing time-sensitive data at the edge of the network, close to where it is being generated. While the foundation of this has been laid already, 2021 will see fog computing gain steam. Indeed, well-architected ecosystems will nurture IoT product development and provide significant value to business.
2021 Outlook: This is especially important in industries where many IoT-enabled smart machines are constantly generating a vast amount of data, such as in a large manufacturing setup. By extending the cloud even more to be closer to edge devices, data analysis can be carried out efficiently and securely. Fog nodes will be deployed close to the IoT devices to carry out analysis quickly and cost-effectively. This will help to avoid latencies that can mean the difference between a massive system failure and the aversion of disaster. For example, a smart car will send critical data for analysis of traffic situations and therefore avoid hitting a pedestrian. In such a situation, low latency is critical since it can mean the difference between life and death. In 2021, this technology will improve and use cases will expand. In our always-on and hyper-connected world of ever-decreasing attention spans, latencies have the potential to significantly mar the user experience of a software product, which is a case for other situations (such as a shooting game) that are not life-threatening as in the example above. This is another reason why the low-latency experience is emerging as one of the requirements of a good software product experience.
Blockchain
2020 Recap: Although Blockchain technology has been around for a few years, the development with this technology has largely been restricted to the cryptocurrency use case. While Blockchain is undeniably the foundation of cryptocurrency, this technology has other use cases in healthcare, supply chain, cybersecurity, and more. Wherever the arises to ensure security and immutability of data, Blockchain can be the ideal tech to use.
2021 Outlook: So far, Blockchain has stalled at the PoC or experimental level. The technology may scale in 2021 with updates and better implementations of smart contracts. Updates to Blockchain tech when it comes to securely exchanging data may mean that it can be used whenever and wherever there is a case of secure, immutable data exchange. Moreover, with pandemic-induced accelerated digitalization, the needs and opportunities for such widespread, immutable, network-approved data exchange has skyrocketed. The potential for this tech to become mainstream is truly staggering. The global Blockchain market is expected to reach $39.7 billion by 2025. Because of pandemic-induced budget cuts, organizations see a need for having the maximum impact and measurable benefit of any project in a short time span. This is why although Blockchain has the potential to disrupt many industries, experimental Blockchain projects are likely to be cut in 2021, and projects that have already shown positive results are likely to be pushed to production.
Green Business
2020 Recap: More and more businesses and governments realized the importance of combating climate change. The world began to move from a “what if” climate change scenario, in which scientists and technologists think about problems that may occur, to a “what now” climate change scenario, in which scholars need to solve climate change issues that are affecting the world today. This is important because it is possible that climate change reaches such a level as to render the costs of managing IT infrastructure either impossible or astronomical. New policies and practices with regards to combating climate change have come to the fore.
2021 Outlook: Current levels of energy consumption by IT equipment and infrastructure have a detrimental effect on our society. This equipment uses power at levels that are unsustainable from a climate standpoint. This happens because this infrastructure relies on chips that require high levels of power to function properly. To solve this problem, researchers believe that all-photonics networks (APNs) may hold the answer. These APNs use optical and hybrid cabling to enable fast, end-to-end transmission of data between a terminal and server. They have the potential to keep quality high and latency low. Most importantly, these networks are not as power-intensive as traditional IT equipment. From a climate point of view, this is ideal because these APNs provide services at 1/100th of the power required by today’s IT infrastructure.
Another important consideration is that the economy is set to shift from a Selling economy to a Renting economy. This means that the economy is set to move from a transactional model of selling products, to a model based on sharing, leasing, and upcycling. This has already begun, with the move towards multi-tenant architectures based on the principles of using shared resources for cost-effectiveness. This move towards sharing resources has significant positive benefits from the point of view of sustainability, since more user needs are being catered to with a smaller consumption of energy. In 2021 and beyond, we will see this trend continue.
Emerging Technologies of 2021
The world will see various technologies in the spotlight in 2021. Let’s take a look at these technologies and the impact they may have.
AIoT
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and IoT are both technologies that have the goal of making machines smarter. In 2021, we can expect to see these merge into what technologists are labelling the AIoT, or the AI-enabled Internet of Things. Connected devices constantly generate vast amounts of data – for example, autonomous cars can generate 1 GB per second. With IoT, you can generate and send vast amounts of data to nodes. With AI added to the mix, this data can be processed and analyzed to generate insights and even make decisions. AI can be thought of as the brain, while IoT can be conceptualized as a large, expansive nervous system.
By implementing AIoT, the system will be able to make autonomous decisions boosting productivity and efficiency. Monitoring aggregated information from sensors and finding correlations that might be indicative of possible system failures empowers systems to make autonomous decisions such as shutting down operations in the event of an emergency. By implementing AIoT, systems will be able to analyze events in real time, detect anomalies, and even predict and auto-remediate cyber attacks. Transactional costs will be reduced due to optimization of processes. With focused insights and faster, more accurate decision making, businesses will see faster growth of operations. AIoT will see various applications in any product and service industry that relies on analyzing vast amounts of data from sensors, such as manufacturing, or engagement with software products, such as healthcare in the case of creating comprehensive patient profiles based on medical history in EMRs and EHRs, and in the wellness industry, for example by gathering, analyzing data from wearable devices.
Progressive Delivery
Progressive Delivery builds on the principles of DevOps and CI/CD. It is the logical evolution of the software deployment process for enterprises that have already implemented agile development processes and have a comprehensive DevOps culture. Progressive delivery enables organizations to continuously roll out new features while limiting the potential negative impact of any failures caused due to the new code.
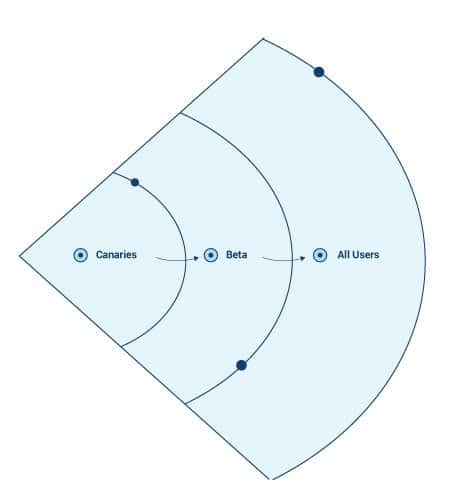
One core tenet of Progressive Delivery is controlled release progressions. This means that a feature is released to a small subset of users, and is toggled on or off using feature flags. The impact of this code release is assessed with key metrics and user feedback is gathered. If there are problems, developers can roll back the feature with the click of a button. If all seems well, the feature can be released to a wider audience. The canary releases, targeted rollouts, and ring deployments all make for a high velocity, low risk delivery pipeline. In this way, developers and product managers can control which users use which features and at which times.
Progressive Delivery is also useful for A/B testing wherein a certain feature can be deployed in two versions. After gathering statistics and feedback about how the feature has been received by end users, developers or product managers can take a call about which version of the feature to release.
Another aspect of Progressive Delivery is the delegation of control. In the beginning, it makes sense for developers to have control of a particular feature since they are the ones building and partly testing it. After the preliminary development has been done and tested, it can be released to a product manager in charge of launching the feature. This frees up the developers to focus on other key tasks. Dive into the details of Progressive Delivery here.
5G
Cellular connectivity is set to become cloud-based and software-driven in 2021. 4G LTE, the gold standard of cellular connectivity in 2020, is set to be replaced by 5G. Although many organizations had plans to roll out 5G in 2020, the pandemic ensured that these plans screeched to a halt. In 2021, therefore, as lockdowns ease and economies start to open, 5G is set to rise on the horizon.
5G, the 5th generation of cellular connectivity tech, has been created to increase connectivity speeds, reduce latency, ensure high availability, and offer a massive network capacity. 5G tech has a peak speed of 20 Gbps, while that of 4G is only 1 Gbps. 5G is designed to connect humans, devices, and machines. 5G is based on OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing), which is a way of modulating a digital signal across several different channels to reduce interference. 5G takes cellular connectivity to the next level by using virtualized and software-driven networks that use cloud technology. 5G will use licensed and unlicensed wireless technologies to build a heterogeneous network that will add bandwidth for users.
5G’s promise of lower latency can improve the performance of many types of digital experiences, such as online gaming, video conferencing, shooting games, and even self-driving cars. 5G tech will help rural areas get online faster and more effectively. Combining 5G with AI-ML will reduce response times to a fraction of a second, which can mean the difference between life and death in the case of self-driving cars. In the healthcare industry, 5G will enable patients to be monitored via wearables that constantly deliver data on key health indicators, such as heart rate and blood pressure. With the promise of low latency, it’s possible that surgeons could control their instruments and perform surgeries remotely. Manufacturing will benefit immensely with 5G due to the fast connectivity that is needed for devices connected to the IoT. 5G network infrastructure will be able to take the load of the massive amounts of data generated by these devices. 5G will also help in super-fast consumer electronics. Read more about 5G here.
Chaos Engineering
Advances in large-scale, distributed systems have increased the complexity and interconnectedness of software systems. Therefore, the types and manner of situations in which problems can arise, have also increased. After all, the more complex a system is, the more scope for problems to occur. Keeping this in mind, the field of chaos engineering seeks to experiment on a software system in production in order to test how the system responds to turbulent conditions. Among other things, chaos engineering involves randomly injecting harm into software systems, such as using a program to randomly cause outages to certain servers or services. Chaos engineering involves experimentation which produces innovation and a greater understanding of the system. It does not entail testing the known details.
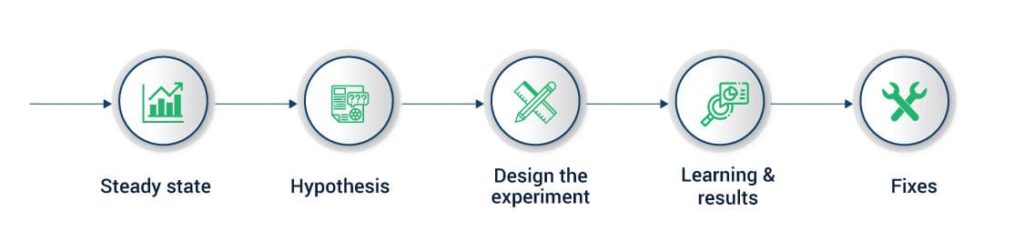
Businesses are increasingly implementing this approach to make their software more resilient. The weak points which are present in the system can be addressed actively. Netflix pioneered this with fault injection mechanisms that actively (but carefully) sabotage their systems to build confidence in the quality of their software. Chaos engineering is set to become more commonplace in 2021 and may be a requirement for robust quality assurance practices. With distributed software architectures, such as microservices, becoming more commonplace, it is quite likely that chaos engineering will become a testing necessity rather than a bonus. This is compounded by a hyper-connected culture that has created an always-online user base that consumes large amounts of data 24/7. The possibilities for system failure, therefore, are immense. To stay competitive, businesses must use tools, such as Netflix’s Chaos Monkey, to carry out this chaos engineering. It’s quite likely that in 2021, other companies will develop their own Chaos Engineering tools, leading to a greater selection of tools. Read about Chaos Engineering principles and best practices here.
Micro Frontends
Micro Frontend means approaching front-end development of web apps with the same concepts as those of microservices. A microservices approach was earlier reserved for the back-end architecture only. Microservices have already become very popular; in 2021, we will see a microservices architecture gain popularity not only for back-end development, but for front-end development as well.
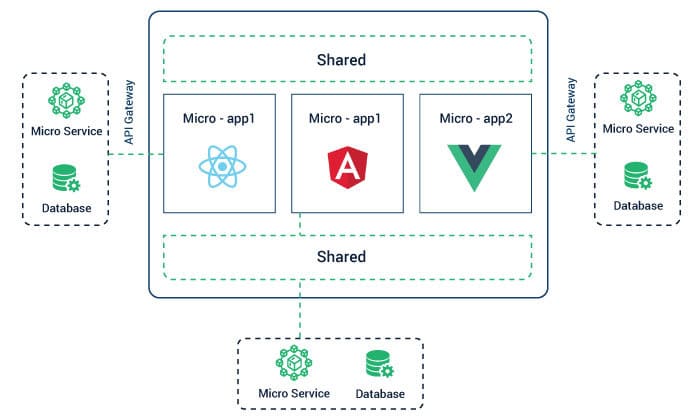
The micro frontend approach is rooted in the concept that a web application is a compilation of independent features that can be developed by different teams and then fused to create a homogenous interface. This involves a cross-functional approach wherein different teams collaborate to create end-to-end features, from the database to the UI. This concept meshes nicely with the rise of ChatOps and agile delivery, wherein fast deployment of code is facilitated by ChatOps, and code deployment takes place quickly. Adopting a micro frontend approach to web application development offers design versatility; the use of different frameworks and libraries, along with a vertically optimized team, means that beautiful, intuitive apps can be developed with a top-notch architecture, design, and functionality. This architecture also provides incremental upgrades due to developing an application in separate parts rather than a whole. This allows developers to quickly upgrade user-centric workflows in an incremental manner. The end user does not feel the effects of in-progress changes due to incremental upgradation of the UX or the entire micro frontend interface. Next, the source code in a micro frontend architecture is smaller and cleaner than a monolith. Because of this, teams can mitigate risks related to problematic coupling of components. The micro frontend approach also involves a continuous delivery pipeline and autonomous deployment. Organizations which already implement CI/CD have a huge advantage here, since they already have the infrastructure and processes in place for integrating Micro Frontends with their current DevOps mechanisms. Finally, by decoupling codebases and release cycles, teams can have exclusive ownership of their specific components without having to depend on others. The independence of operations also makes the workflow quicker. Because of all these benefits, Micro Frontends are set to become more popular in 2021. Read more about Micro Frontends here.
Pipeline as Code
Pipeline as Code is a concept built off DevOps and the need to decentralize the application building process. Pipeline as Code helps to simplify the creation of deployment pipelines and also reduces several overhead costs. It also helps to track changes, increase productivity, and reduce breakdowns. Pipeline as Code means that the configuration of delivery pipelines should be treated as code. Their code should be in source control and the pipelines should be modularized in reusable components with automated testing and deployment.
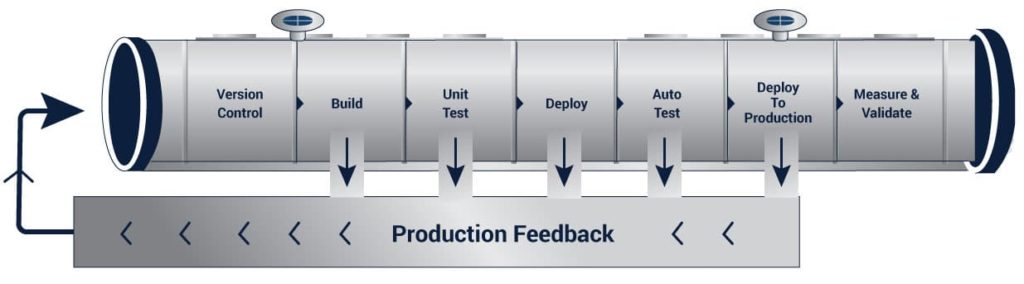
This will be especially important in 2021 due to the move to a microservices-based architecture and decentralized, autonomous teams. To implement Pipeline as Code, technologists have started to come up with delivery pipeline templates and tooling that enable standardized deployment of services and applications. Such tools use a declarative model of pipeline delivery, in which the pipeline blueprint is defined for stages such as build, test, and deployment. The implementation details are abstracted away. Jenkins is a very popular and useful tool for Pipeline as Code. In 2021 and beyond, many other companies may build tools that perform a similar function.
By implementing Pipeline as Code, you can reduce manual intervention by coding the entire pipeline. This is contrasted with the earlier ways of manually configuring CI/CD tools to get a new pipeline running. By coding the pipeline, you can collaborate faster and pipeline updates are automated. Next, version control becomes easier. You can track pipeline history in real-time and the risk of problems due to unauthorized changes is mitigated. If you lose any data, the data can be restored due to version tracking. All these benefits mean that in 2021, organizations will likely implement Pipeline as Code in their processes. Read more here about implementing Pipeline as Code with Jenkins.
The Hybrid Cloud Future
While hybrid cloud is not a new concept, we will see the adoption of this rise in 2021. This is in part due to the tremendous disruption caused by the pandemic and the resulting acceleration in the move from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud. Hybrid cloud environments are a combination of on-premises and cloud. This is in contrast to multi-cloud, in which multiple clouds are used and on-premises infrastructure is not used.
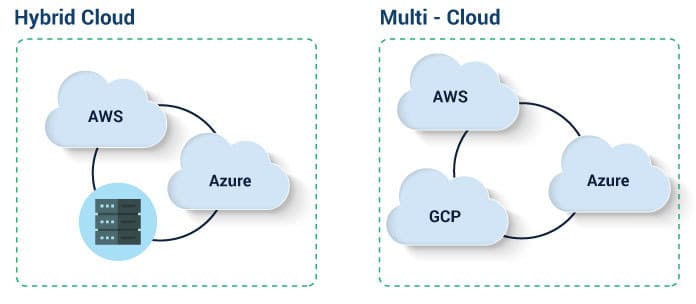
As cloud systems have matured, organizations have realized that there is no magic one-size-fits-all solution for migrating to the cloud and reaping the benefits therein. To solve this problem, many organizations are likely to shift to a hybrid cloud model. This offers the best of both worlds, in which organizations get the flexibility and convenience of the cloud along with the security and privacy that comes with on-premises infrastructure. Content delivery, for example, can be done via a public cloud and sensitive data can be stored on-premises. Hybrid cloud environments allow users to select the combination of services that best suits their needs. This means that cloud providers may also begin to rethink their modes of delivery. In 2021, open source tools are set to help integrate multiple clouds and on-premises systems into a single hybrid platform. This means that it will be easier for non-programmers and those without a lot of hybrid cloud expertise to adopt an application deployment model that’s easier to use. This will mean that hybrid cloud experts will be free to work on other, higher-value projects. Another breakthrough expected in 2021 is the integration of AI, IoT, and the hybrid cloud. AI is set to see a surge in its scalability and commercial availability. Coupled with advances in 5G tech and connected devices, AI computing at the edge could merge cloud and edge computing. This would mean a key technological upgrade for hybrid cloud.
DevSecOps
DevSecOps is another offshoot of DevOps. DevSecOps is a DevOps practice that integrates security right from the beginning of the software development lifecycle. It involves automating some security gates to prevent the DevOps flow from slowing down and ensuring the smooth execution of the entire DevOps pipeline. DevSecOps is all about built-in security. If security is relegated to the end of the development lifecycle, organizations can find themselves gone back to long development cycles they were trying to avoid in the first place. Automating security checks is key to DevSecOps.
Many businesses incorporate security far too late in the development lifecycle. Organizations have started to realize the downsides of this approach. For example, organizations may miss security threats early on, and this would result in adding security to the development process far too late. Although security practices may reduce the speed of software deployment, organizations have realized that the benefits of implementing comprehensive security practices far outweigh the risks of deploying software slightly late. These two seemingly conflicting goals can be reconciled with security tools that can be automated and integrated at the code commit and pre-implementation stage. In addition, DevSecOps can do this without slowing delivery. With DevSecOps, security issues are identified as they are encountered and not only after a threat has occurred. Ultimately, with DevSecOps, companies are realizing that they can reduce technical debt, build a friction-free operational environment, and shift left in terms of security. Because of these benefits, DevSecOps is set to become more mainstream in 2021.
Upcoming Programming Languages
Legacy programming languages, such as Java and C++, have started to show their negatives. For example, Java is finding it difficult to keep up with modern software development needs and C++ has become more bloated by adding more features. Modern programming languages are free of this baggage and are better designed to fulfill the modern developer’s demands. These newer programming languages focus on developers’ ease of use, as well as features such as type inference, null safety, and conciseness. Many of these languages are designed to make full use of modern infrastructure and hardware, such as a variety of cloud computing models.
According to the Stack Overflow Developer Survey, about 86% of developers code using Rust. This is currently the most popular programming language, and will continue to gain popularity in 2021. Indeed, Microsoft declared that they will be using Rust to fix security bugs. Amazon will invest heavily in Rust due to its superior runtime performance and lower costs of testing and validating Rust implementations. Other languages set to grow in their popularity include TypeScript, Python, Kotlin, Go, Julia, and Dart. Go is already established and its popularity is set to grow with the Go 2 release. In Android app development, Kotlin has surpassed Java. TypeScript has established itself as an alternative to JavaScript, and is set to gain popularity in the future. Apple’s Swift has begun to replace Objective C as the preferred language in the Apple ecosystem. The popularity of all these languages is set to rise in the future.
Looking Ahead to 2021
The tech trends set by 2020 are well on their way to continue to influence business in the next year. Although the world screeched to a halt due to the pandemic, the silver lining is that the adoption of tech trends accelerated because of the forced work-from-home model. With tech-related to Fog Computing, Blockchain, Micro Frontends, DevSecOps, AIoT, 5G, MLOps, and more coming to the forefront, 2021 will see procedural and cultural shifts in line with the (forced?) adoption of these technologies. With the traditional office set to undergo a massive shift in its role, we will likely see offices become fully tech-enabled places of meeting, collaboration, and socialization.
If you would like more information about any of these topics, or if you would like to understand how to incorporate other new-age technologies into your software product, please reach out to us at info@34.200.212.66.
