The world of tech today has become a lot more advanced, experimental, and playful than it was when Enterprise Technology ruled the roost. And naturally, the Internet has played a pivotal role in this transformation, which extends to DevOps dynamics governing how products grow and spread. Today, we operate in a multi-platform, multi-cloud, hybrid world, where deployment targets and routes have to be fluid and dynamic.
So far, Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) has been at the centre stage of DevOps Services, steering the modern software development industry forward. However, the current and future demands of the industry require new practices that make the deployment process progressive.
And that’s exactly what Progressive Delivery has to offer!
Leveraging a mixed bag of technologies and skills for software development testing and deployment – A/B testing, Feature Flags, Blue-Green deployments, and canarying, to name to a few – it transforms the approach toward service and application delivery.
And all this to an extent where deploying a service doesn’t necessarily mean releasing it.
Moving Fast With Control
Progressive Delivery refers to a new lifecycle of software development that is deployed to ship code faster and at reduced risk. Thus, always delivering on improved customer experience. It is essentially an extension of the core tenets of CI/CD equipped with safeguards and controls that exponentially cut the risk of continually pushing code into production.
As such, control is at the heart of Progressive Delivery. This control extends to features users can see, the timing of changes deployed by engineers as well as the authority of releasing features. To delivery on this element of moving fast without losing control, Progressive Delivery relies on two core principles:
-
Release progressions
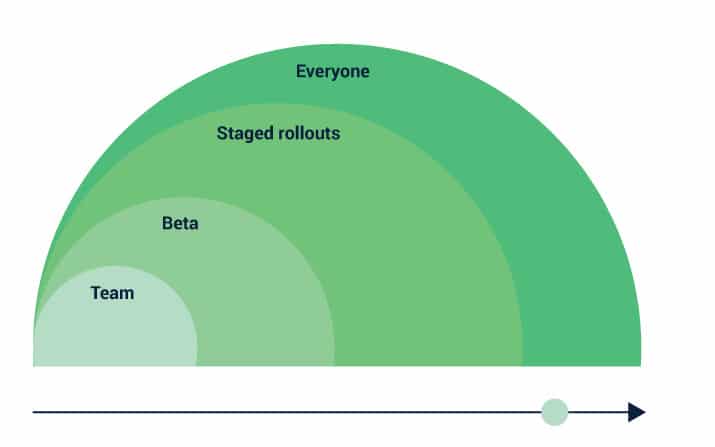
Adjusting the number of users who gain access to new features at a pace that your business can handle. This control can be exercised through percentage rollouts, ring deployments, canary launches, or targeted rollouts. This facilitates the creation of multiple checkpoints for experimenting, testing, and assimilating feedback. These elements can then be used to improve the quality of every new feature – and by extension, the entire product.
-
Progressive delegation
This entails delegating control of a new feature in a progressive, phased manner. Simply put, in the beginning, the control of a feature rests with the engineers tasked with building and testing it. After the testing, it may be released to a product manager in charge of launching a feature to the end-users. The product manager, then, controls the release process, freeing up the engineers to focus on product development and testing for other projects.
The versatility of Progressive Delivery makes it the right fit for all kinds of users, even those who have not adopted CI/CD in their processes. Once adopted, it can be deployed as often or intermittently as an enterprise deems fit.
The Evolution of Progressive Delivery
To understand the evolution of Progressive Delivery, one has to look back at the evolution of software development lifecycles, going back to the Waterfall days where software developers would spend months developing a product. Despite the meticulous and thorough approach, the products were often far from perfect.
Then came the Agile principles, followed by CI/CD. These models transformed the speed and accuracy of software development, testing, and release. With the tech ecosystem becoming more dynamic, even an advanced approach like CI/CD was found to be lacking something.
Then, speaking at QCon London in 2019, RedMonk Founder James Governor floated the idea of enhancing system resilience through Progressive Delivery. It sought to mitigate the risk that comes with shipping code – often unfinished – several times in a day. Software companies wanted a security net to safeguard their users from the high-risk of failures that come from shipping changes frequently.
More importantly, they sought a system that could deliver the right changes to the customers at the right time. That’s exactly what Progressive Delivery offers.
Using a mix of A/B testing, Feature Flags, Canarying, Istio service mesh, and Kubernetes, Progressive Delivery enables a sophisticated system of routing new application features to end-users quickly and securely without losing control.
The Need for Progressive Delivery
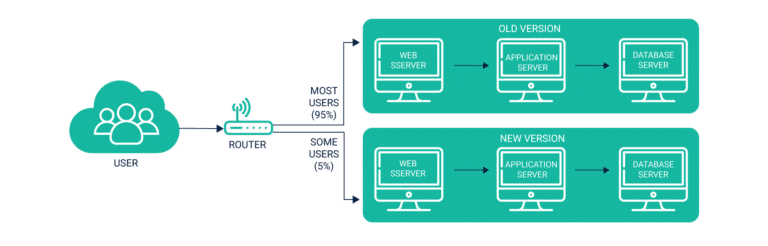
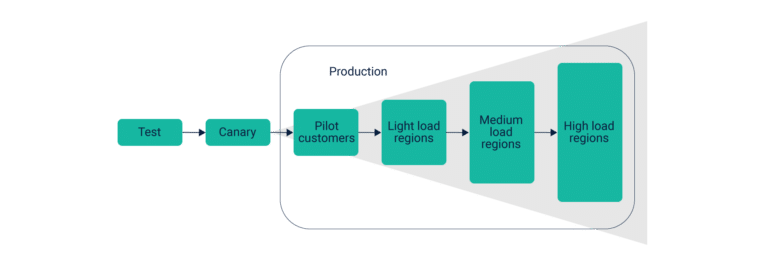
Progressive Delivery allows you to deliver any change to a select group of low-risk audience, assess their reaction, make changes if necessary, before expanding to a larger user pool. For instance, a target group of 1% of the total user base is first exposed to any new changes. This pool is then expanded to 5 to 7% before delivering changes to the entire userbase.
In case, the changes are not well-received by the users, it affects only 1% or 7% of the traffic – and revenue – rather than 100%. This system works on the principle of controlling two corresponding factors – environment and users. Tools such as blue-green deployments or canary builds are used to limit exposure to a new change.
All leading tech behemoths, be it Google, Microsoft, Facebook, or Amazon, deploy Progressive Delivery already by rolling out any new products or features to a small market or a percentage of users in a market to gauge how well it is received.
For instance, Microsoft relies on ring deployment to control their releases by dividing different user groups into groups for different stages of a rollout. They start by testing a new feature with the canary group or ring zero. Only after all performance indicators are satisfactory in the canary group, do they roll out the feature to the next group or ring and the one after that.
Similarly, Github uses feature flags to unveil their new feature to in-house users before revealing them to the world. Only when a new feature delivers satisfactorily on performance parameters for this select group is it rolled out for the remaining users.
In both approaches, Progressive Delivery allows gaining actionable insights from valuable data and user feedback to improve on features and functionalities.
Key Elements of Progressive Delivery
The Progressive Delivery system is built upon a well-structured network. Some of the key elements of which are:
-
Canary Testing:
This means releasing any new change or feature to a small set of users. This allows a speedy check of the impact and effectiveness of the changes and also the users’ readiness to embrace the change. Since canary testing allows new code to be deployed to a small fraction of users (often 1-5% of the entire user base), the server traffic can be closely monitored to assess performance and spot unexpected issues. In that sense, it can be considered a subtler variant of the blue/green deployment method.
-
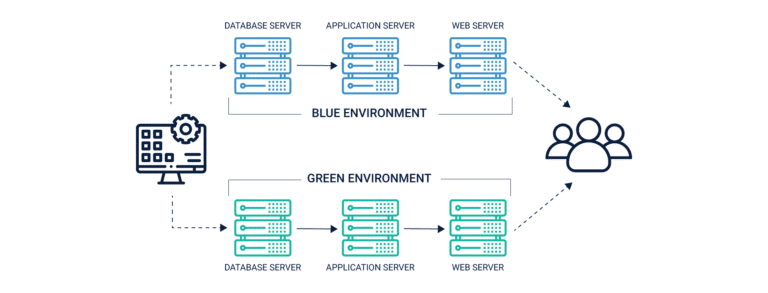
Blue-Green Deployments:
In this deployment method, any new change feature is first rolled out into one production environment (blue). Once its effectiveness in this environment is tested, it is then shifted to the other environment (green). At a time, only one of these environments is live. It serves as a testing ground for changes rolled out, facilitating a quick rollback in case of any glitches. By running two identical production environments, the downtime and risk can both be controlled effectively.
-
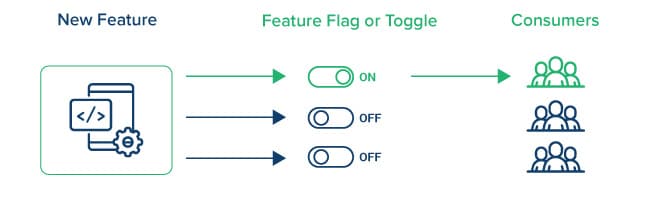
Feature Flags:
Feature Flags or Feature Toggles facilitate enabling, disabling, or hiding certain features from the user interface. This element of Progressive Delivery helps in testing changes and new features with a select group of users before making them available to a larger audience.
-
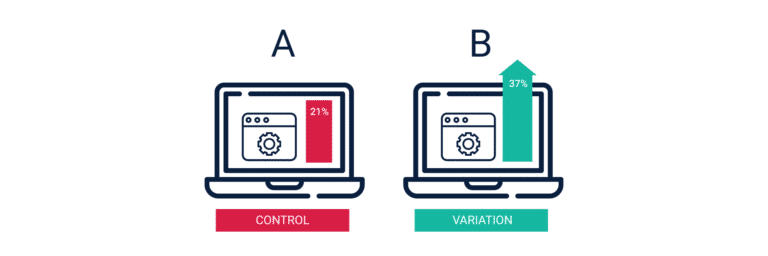
A/B Testing:
This is used to test different versions of a change on different groups of users and then assessing which one performs better. A/B Testing is most commonly used to check the impact of any changes on the usability, which may in turn impact conversions.
-
Observability:
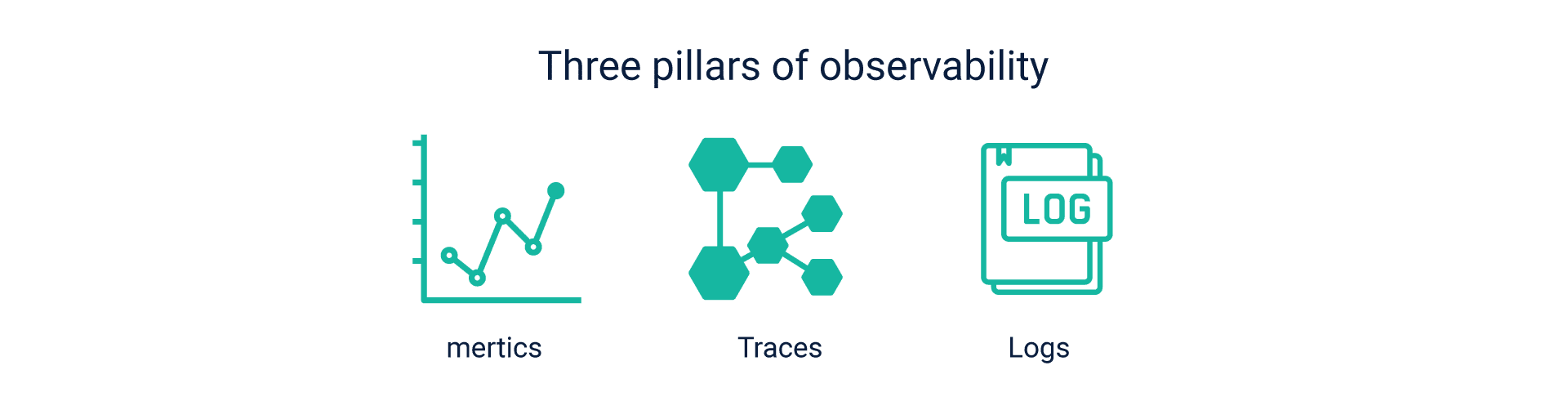
This element focuses on assessing management in production using parameters such as metrics maintenance, tracing, and logging. It is a departure from traditional monitoring techniques in the software world. As the name suggests, observability is all about seeking answers regarding a system’s performance just by observing it from the outside. In progressive delivery, this translates as answering questions without the need to ship new code.
-
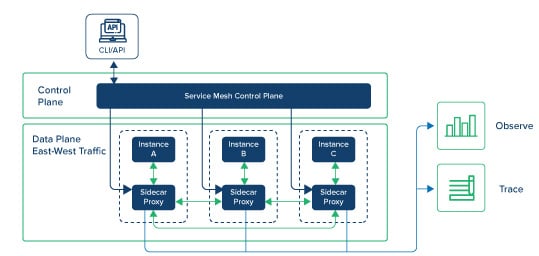
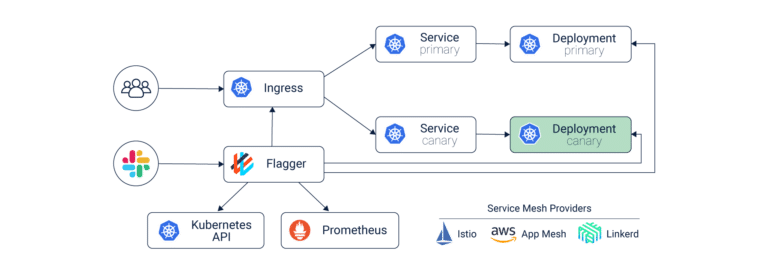
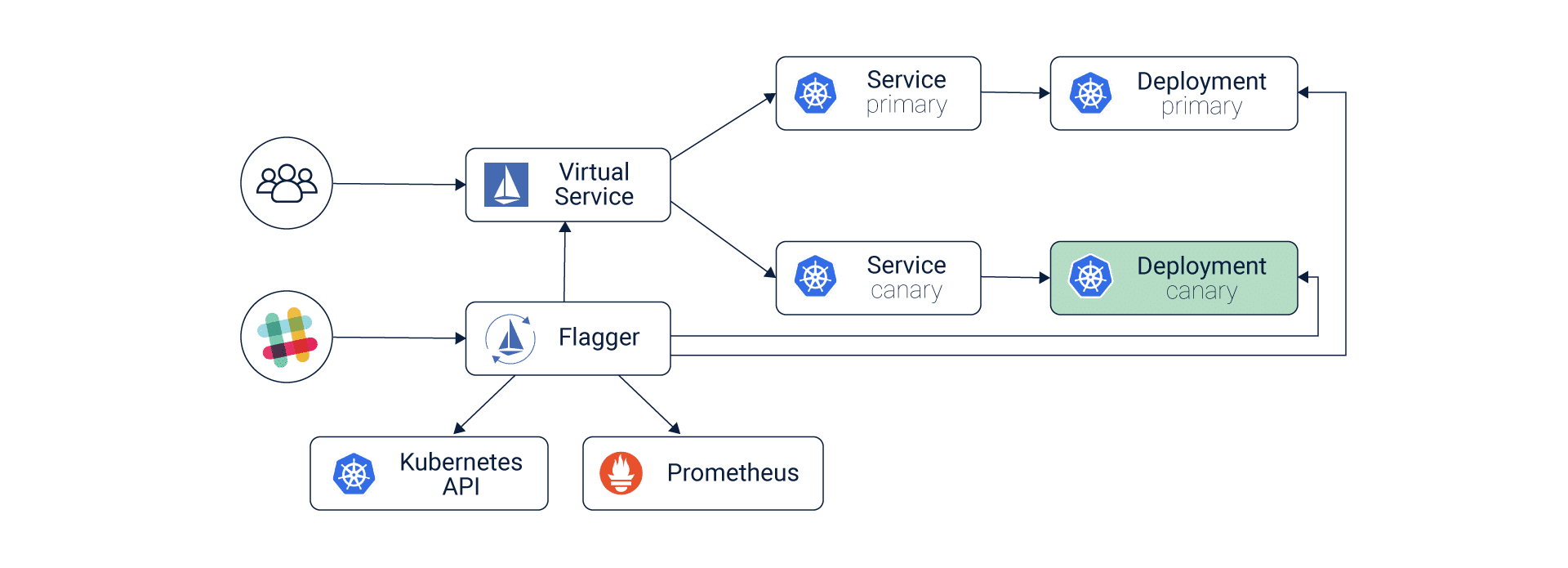
Service Mesh:
A service mesh, placed between containers and services, logs what worked last. This helps in reverting to a previous response if a new change does not work. Service mesh is responsible for enabling user segmentation, traffic shifting management, metric maintenance and observability. By controlling these elements, it allows users to closely control the blast radius.
-
Chaos Engineering:
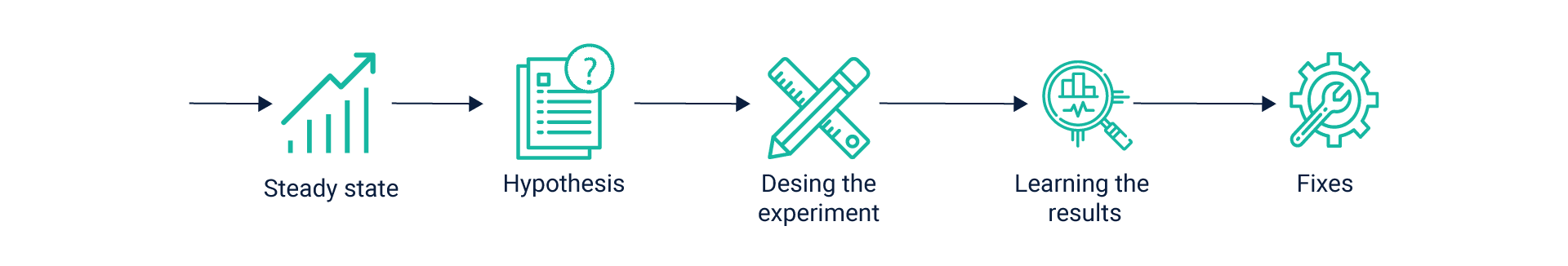
Chaos engineering is all about embracing a failure through defining the normal state for a system and then using actual resistance testing to iron out the problem areas. This allows businesses to run a controlled experiment on their digital products and services during development, testing and progressive delivery. Developers and delivery teams can address shortcomings and issues proactively, contain SLA breaches with minimal downtime. This not only helps contain the negative impact of any glitches on business but also gives them the confidence that their systems are equipped to function optimally in real conditions.
Benefits of Progressive Delivery
Progressive Delivery allows your development team to stay in control of a rollout process. This translates into the following benefits:
-
Quality Control:
Through elements such as chaos engineering and service mesh, Progressive Delivery allows developers to exercise quality control even as features are being rolled out.
-
Foreseeing Failures:
When any new change is rolled out in a phased manner using canaries or feature flags, with its functionality being tested at every step of the way, any functionality issues based on the experience of a small pool of users can be flagged and corrected.
-
Revamping Changes:
Based on the feedback of the users exposed to new features or functionalities, any changes that aren’t working can be quickly reverted or revamped.
-
Reduced Risk:
Since the developers are in total control of the rollout process, it mitigates risks and facilitates a greater focus on development.
-
Delegation of Control:
The progressive delegation of control of any new feature places the task of release in the hands of product managers or other non-engineer professionals. This frees up the developers to swiftly move on to other high-priority projects
-
Embracing failure:
With chaos engineering, Progressive Delivery not only gives developers the ability to foresee failure but also embrace it, accommodate it and quickly fix it using actual resistance testing.
-
Reducing Downtime:
In a recent study, Expedia linked new changes to two-third of their outages. With a Blue-Green deployment model, Progressive Delivery reduces the annoying downtime or unresponsiveness to a minimal.
Best Practices to Implement Progressive Delivery
The system of Progressive Delivery was conceived to roll out new updates or features without losing control of the impact of this change. For instance, if a new code is being released, every new division exposed to this change becomes a part of its blast radius, creating a ripple effect that carried the initial impact forward.
In this ecosystem, Progressive Delivery acts as a valve that can separate deployment of code from a release, thus, controlling its trajectory as and when it is made available to the end-users. To make it effective, the point of checks and control need to be driven by feedback and data-driven insights.
To leverage this cultivated approach for optimizing the continuous delivery pipeline, the following practices are a must:
-
User Segmentation:
Dividing your user base into different groups or canaries, and gradually releasing features in a controlled manner. First to your internal team, then to beta testers, then a selected market or group of users within a market before opening it up to your entire user base.
-
Traffic Management:
Progressive Delivery must also be used to control what section of your traffic you expose to any new changes. Doing this allows you to contain any backlash in case of errors, performance spikes, or rollback. If you detect a problem when the rollout is at 1% of your traffic, you can stop the change in its tracks. This way you have only negatively impacted 1% of your user experience – and perhaps revenue – rather than 100%.
-
Resilience:
You are not leveraging Progressive Delivery until you use to make your processes more resilient. By using the different elements of this system to set up a structured delivery process, you can not only cut back on risk but also determine the best possible user experience through iteration.
-
Slow Rollout:
Users typically resist any changes to an application interface because it challenges familiarity and comfort of use. For instance, when Google tweaks Gmail features, we instantly dislike it. But by allowing users to adopt the changes at their own pace, Google makes the transition easier. Such slow rollouts, couple with a soft nudge through constant reminders, is a smart approach to using Progressive Delivery effectively.
The Way Forward
Progressive Delivery is poised to change the DevOps ecosystem. Naysayers may denounce it as CI/CD 2.0 but the bottom line is that this system will drive changes released in the future based on data insights and an understanding of your audience’s experiences. It is all about shifting focus from grand ceremonial releases to small, significant, and constant changes. Embracing it today means preparing your team to ride a futuristic wave of the product journey.