Edge computing is not just the latest trend but has actually started to give results. If you plan to optimize your current products or want to build an IoT app for your business, edge computing should be an approach that can help you gain a competitive advantage.
The amount of data generated by digital devices is escalating day by day. As the proliferation of IoT devices advances, the cloud is becoming too costly, and it is not fast enough. This is where edge computing comes in.
Edge computing reduces the workloads on the cloud. The computing workflows are shifted to local IoT devices like smartphones of a user. It reduces the long-distance connection between clients and servers.
It is the latest problem-solver for the Internet of things. Edge Computing enables speedy analysis and processing of data. Hence, making the whole process more efficient.
What is Edge Computing
Edge computing aims to speed up critical data processing closer to where the device is located. It Implies that data processing is done more efficiently. There is no need for the centralisation of attributes. In other words, edge computing is a mesh interface to process and store micro data centres locally.
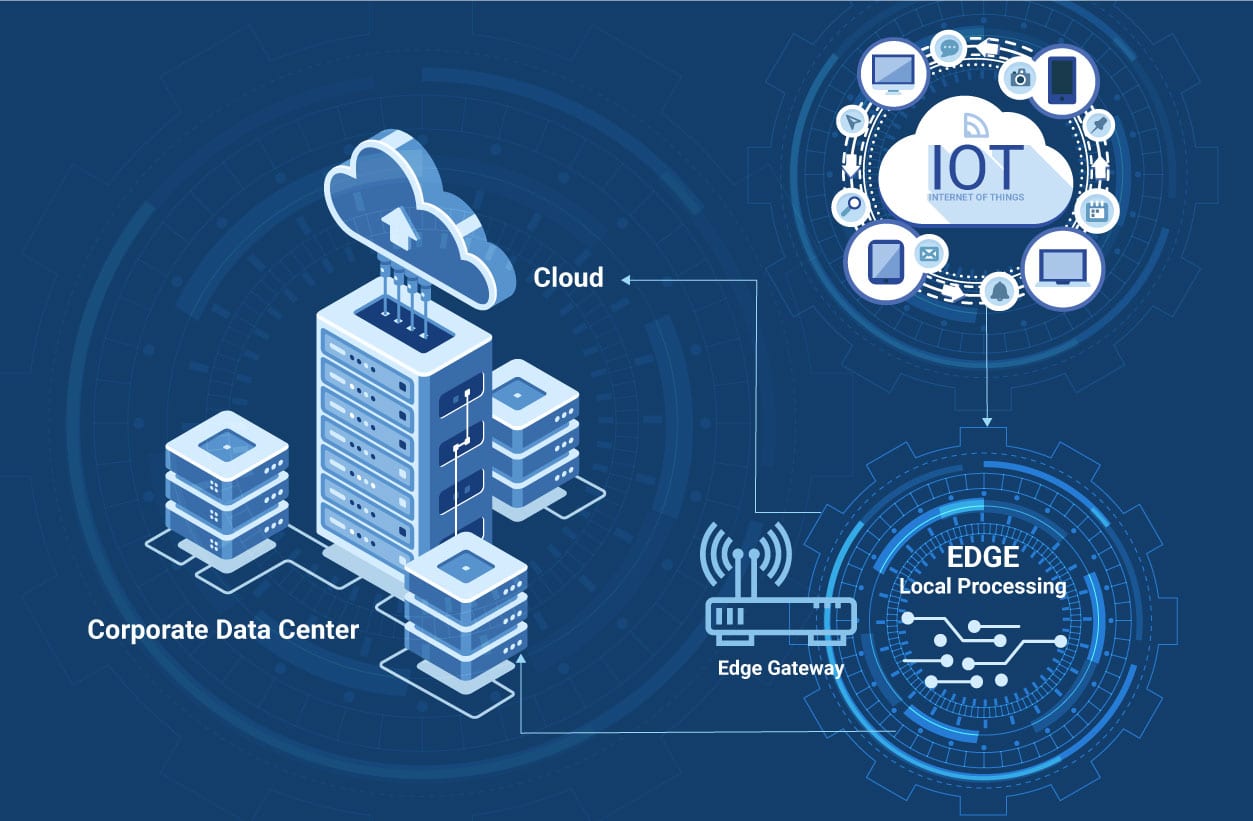
As we understand about edge computing, another term which is catching on is Fog Computing. Fog computing introduces the network nexus between Edge devices and the cloud. Fog incorporates edge Computing along with the network for data processing at its final destination.
Both of these technologies push the intelligence closer to the source of the data. They both are essential when there is a need for real-time data analysis.
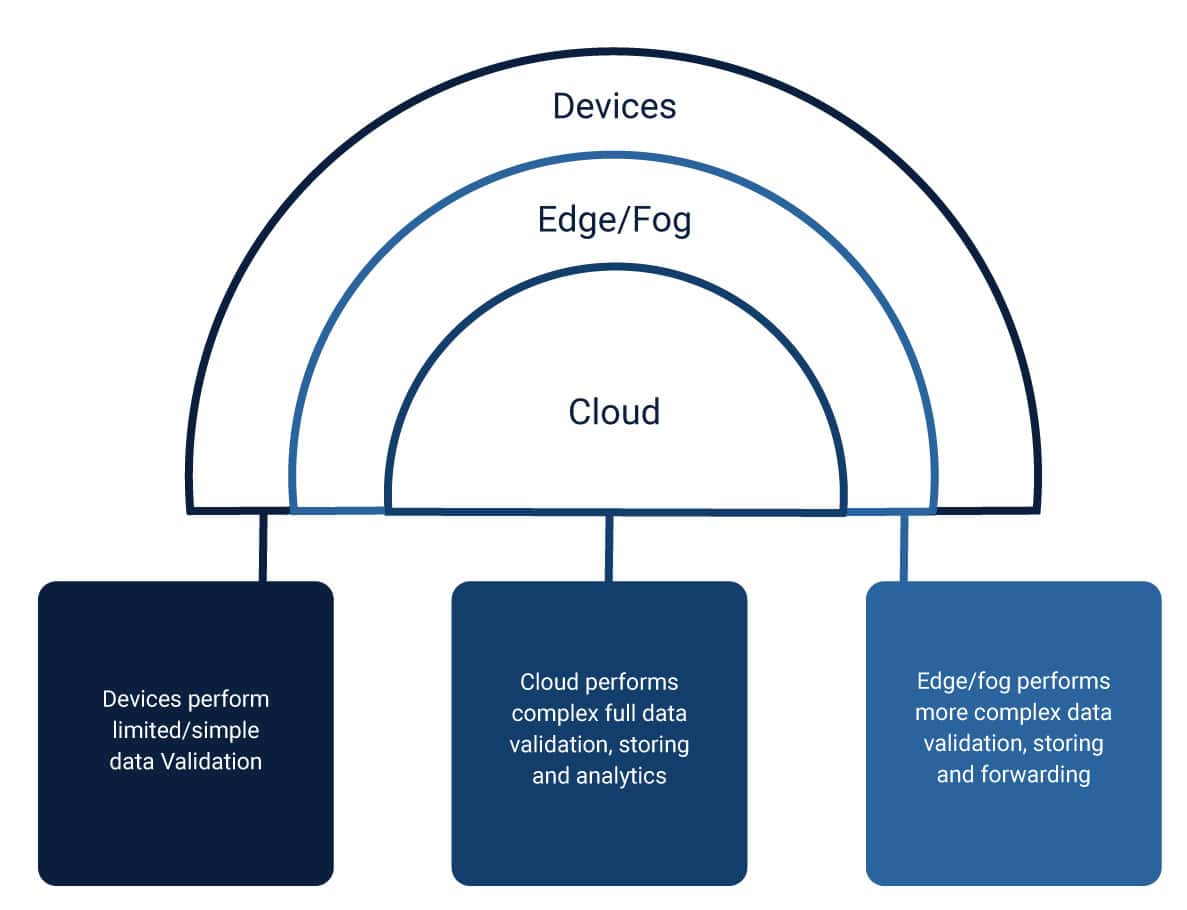
Why Edge Computing?
Many industry verticals rely on Cloud computing to handle their workloads, but it has some drawbacks when it comes to IoT.
- Data security threats:
In cloud computing, data traverses back and forth between a device and the cloud. It increases the risk of privacy violation and data security. - Operational costs
The operation cost escalates as the amount of data processed and shared amplifies. - Performance issues:
IoT applications rely on real-time activities. In Cloud computing, latency increases because of the distance between the server and device. In some cases, the IoT devices have poor connectivity, and they are not able to remain connected to a central cloud.
Industries like finance, manufacturing, telecommunications and healthcare need real-time data analysis. There are many scenarios where speed and fast data is critical in this hyper-connected world.
Edge computing does that by streamlining the flow of data traffic from IoT devices.Edge computing comes handy in many circumstances. The circumstances and extent of the project decide the response time of data. Aggregated and analysed data enables us to take faster decisions.
The data can become more valuable when leveraged and immediately analysed. We live in times where having right insights fast enough can have enormous consequences.
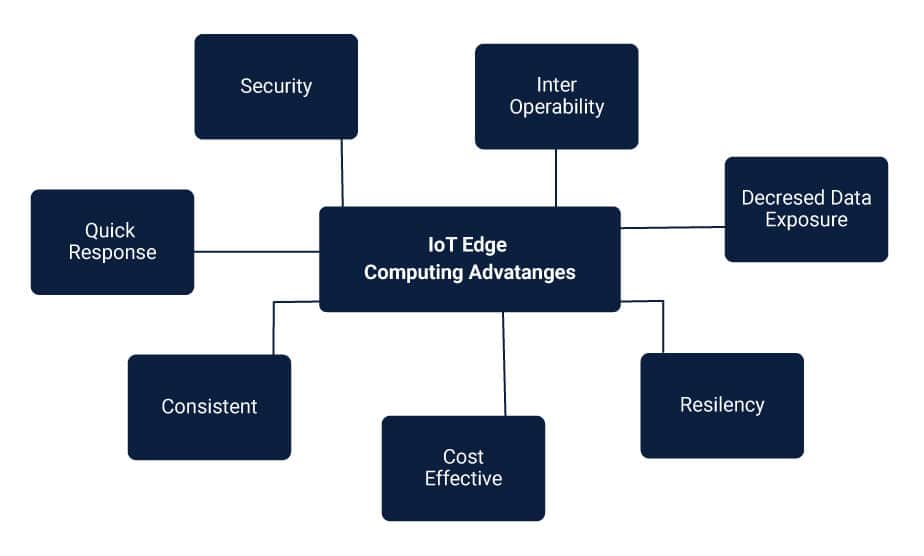
There are many issues which edge computing promises to solve. Let’s dive deeper into its benefits:
- Low Latency:
Edge computing is beneficial in situations where latency is untenable. It reduces latency because it doesn’t travel over a network to the cloud or data centre for processing.Latency is the time taken for data processing and analysis. The response time of a connected devices to the internet is less than a second.
In many situations, the response may be late or interrupted. It happens if there is a glitch in internet connection, or the location of the data centre is distant from the device. The data processing speed is hampered in such cases. Thus, compute resources should be local to counterbalance the latency in transmitting data over distance.
For instance, in a car crash, the car sensors figure out where there is the possibility of an accident and determine the precise time frame to deploy the airbags. If there was any lag or delay in the transmission of data over longer distances, then airbags will not deploy timely. This scenario will not be safe at all, and that’s where edge computing kicks in.
- Data security threats:
In cloud computing, every device is connected to the cloud, and raw data is processed over the internet. It can lead to security, privacy, and legal repercussions, especially for sensitive information.For Instance, many countries hesitate to disclose confidential IoT data outside their boundaries. Edge computing can delete this threat by processing data close to the source. So, administrations can keep the data within their borders and ensure compliance with data sovereignty regulations. These regulations provide citizens with more control over their personal information. - Bandwidth issues:
Companies use cloud computing to process and analyse vast amounts of data. In the case of IoT, massive amounts of power and bandwidth are needed to send the data to the cloud.
IoT devices which generate data and run software should be connected to the cloud to collect and process the data. Edge computing permits businesses to lessen their internet bandwidth usage. The large amounts of data can be managed near the source.
For example, Law enforcement agencies can deploy edge-computing cameras with reduced bandwidth. Massive volumes of video and audio recordings from cameras can be analysed in real-time. - IoT security issues:
Even though the cloud provided excellent security for their IoT applications, but organisations express their apprehension over the safety of their sensitive data. They think once the data travels to the cloud and leave the walls of their company, it will not be safe. Edge computing can solve this issue as more security can be added at the edge. It will make the data storage and processing more stronger against intrusions and hacks.
For example, security can be updated on edge devices. Any outage will be limited to that device and its local applications. - Bandwidth cost issues:
IoT devices generate vast volumes of data and send unnecessary small updates to the cloud. This process requires more bandwidth and hence, the cost of bandwidth increases. The expense of the device to get to that bandwidth and the storage and the analysis costs increases. With edge computing, this data can be acquired and analysed locally before sending it to the cloud. It will be much affordable as compared to sending unfiltered data over costly WAN links. - Scalability:
In edge computing, data processing is decentralised, placing less load on the network. If application and control planes are at the edge next to the data, then computing IoT devices have less resource impact on the system. - Better app performance:When data is processed and stored near the source, the lag time is reduced. It improves app performance.
Use cases for IoT Edge
Data processing and analysis speed are indispensable in many industrial IoT applications. They also play a pivotal role in industrial transformation. Automation is the next stage of the industrial revolution. Edge computing makes it more accessible.
Few Use cases and examples, which take full advantage of edge technology are:
- Device Management:
Many device traits and structures can be managed at the edge. Most device management platforms extend their functionality by connecting devices to edge infrastructure. Few distinct attributes which can be supported by the device management at the edge are:
- Distributed firmware updates:
The edge gateway can be utilised for the local distribute firmware updates. In this scenario, the distribution is managed by the edge node. Whereas, in cloud computing, a queuing system distributes the firmware update centrally. - Diagnostics of connected devices:
Specific problems with the devices can be recognised using analytics at the edge. Machine learning or pattern recognition plays an important role. - Device configuration updates:
The devices at the edge have to be arranged locally when the services change. The edge can remotely manage it.
2. Priority Messaging:
Most of the data generated by the IoT is low priority data and has more economic value. Sometimes there is some critical data which should be prioritised and immediately acted upon. The expanse of priority messaging is not limited to single applications.
It can launch a cascade of actions across different devices and applications. Examples of priority messaging include:
- Transportation:
Priority message of collision alert needs to be sent to the vehicles. It enables the automobiles to avoid the crash. - Environmental:
Priority messages for pollution or rainfall above safe index. - Health & Safety:
Priority messages for a fire alarm for building evacuation. - Security:
Priority messages for security actions in case of unauthorised activity, e.g. drones when flying into no-fly areas.
3. Data Aggregation:
More data generate as many IoT devices are connected. More data results in more replication of data from those devices. For example, reports of many vehicles stuck in the same traffic jam. All this data is replicated, and not everything needs to be sent back to centralised servers. Edge aggregates the collective data from various sensors and selects which data to send.
Another example is that Edge can aggregate the data from many temperature sensors in the same location and produce statistical measures. There are several benefits of IoT data aggregation before sending it onto the core:
- Improving network efficiencies:
Data aggregation can remove the need for data replication and data processing multiple times. It all means a lesser load on the core infrastructure.
- Latency improvements:
Processing lesser data means quicker decisions and faster appropriate actions. Latency will improve by reducing the amount of data for communication and processing.
- Richer data sets:
Aggregated data provides valuable data sets. This could aid machine learning in making more reliable predictions. It will also help in easy identification of patterns and trends.
4. Cloud Enablement:
The edge offers the attractive potential to cloud vendors as it advances better data storage and processing power. Edge can support their higher systems availability and can reduce the load on their existing data centres. A mutually beneficial relationship between mobile operators and cloud providers should exist at the edge.
5. IoT Image and Audio Processing:
IoT edge introduces new ways of analysing the data provided by devices like cameras, including microphones and CCTV, without backhauling the entire audio stream or image. It is beneficial in many IoT applications, like monitoring noise pollution or reading a licence plate.
An edge cloudlet can process the image, audio or video data for the determination of critical information, like licence plate numbers. Only a small amount of data, like the licence number, is forwarded to the cloud and stored. The camera can be employed as a sensor for monitoring many aspects of IoT in industrial domain like observing power lines from a drone. Few benefits of this use case are:
- Low cost:
Microphones and camera are relatives less expensive to get, install and sustain for the insights. Incorporation of edge computing technology also means easy management of network costs.
- A massive reduction in network backhaul:
The amount of data communicated back to the cloud core can be considerably reduced.
- Quick decision making:
Fast processing makes it possible to support a broader range of real-time applications and yields rapid decisions.
6. Healthcare Devices:
Health monitors and devices keep a check on the patient’s chronic condition. They can save lives by sending instant alerts in case of an emergency. Also, robots can quickly analyse data to assist in safe and accurate surgery. If these devices rely on transmitting data to the cloud before making decisions, the results could be fatal.
7. Security Solutions:
Emergencies and threats demand immediate and necessary response actions. So, IoT edge can be beneficial in the security surveillance system. Security systems can identify the potential risks and alert for unusual activity in real-time.
8. Retail Advertising:
In Retail advertising, edge computing technology can be beneficial in protecting user privacy. It can encrypt the data and keep it closer to the source instead of sending the unprotected data to the cloud. For instance, Targeted ads for retail establishments like demographic information.
9. Smart Speakers:
Smart speakers empowered with edge IoT will be able to understand voice instructions locally to run basic commands. For example, turning the lights on or off even if there is no internet connectivity will be possible.
10. Video Conferencing:
A slow link to the cloud can cause various video conferencing failures like frozen screens, poor video quality, and voice delays. The quality problems will be reduced by employing the server-side closer to the users.
11. Autonomous Vehicle Industry:
Self-drive cars are the next big thing in technology and the automobile industry. Many industry giants are betting big on self-drive cars. According to Gartner reports by the year 2025, more than 1 TB of data per month will be uploaded to the cloud by Autonomous Vehicles.
Edge computing in sync with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and 5G will enable autonomous vehicles to gather data, analyse it. These vehicles will be able to make logical and intelligent decisions in real-time. 5G technology will ensure high-speed data transmission between communication towers and automobiles. Edge computing, along with AI, will empower the vehicles to process and share critical data between cars and broader networks. Real-time and almost zero latency decisions and actions will be the outcome.
To Sum it Up
Edge computing pushes the processing power, intelligence and communication competencies directly into devices. Edge computing is essential for IoT and speed, data, and analytics are vital. IoT edge offers substantial potential gains for mobile operators, their customers and partners.
It focuses on managing many devices and the high volume of data that they generate. IoT guarantees faster data processing and less operational complexity of device management. This technology will result in lower dependence on the cloud and better control of the massive deluge of data.
Edge computing delivers quantifiable value in many industrial and consumer IoT use cases.
Almost-zero latency for critical applications will also happen. Many verticals can profit from IoT edge.
Smart cities and factories, intelligent transport, energy companies and more can experience data processing and storage at the edge. Mobile networks can profit from IoT edge as it reduces connectivity costs. It only transmits relevant information instead of raw data.
The integration of different verticals will happen. For instance, intelligent buses being routed to where the large groups of people are waiting. It will all be possible with the low latency and high-speed data processing capabilities at the edge.
Businesses should deploy edge computing for their use-cases to meet the demands of innovative products. The launch of first services with dedicated IoT applications and tools will result in new opportunities.
