User experience, or UX, is one of the important segments of tech development that focuses on the value of communications among the users and the products they use. Apart from meeting all the technical specifications, UX professionals are always concerned about their products, its structure and design to see if they appeal significantly to their defined set of customers. In this blog, we will discuss different phases in UX designing and see why they play such an important role in product development cycle.
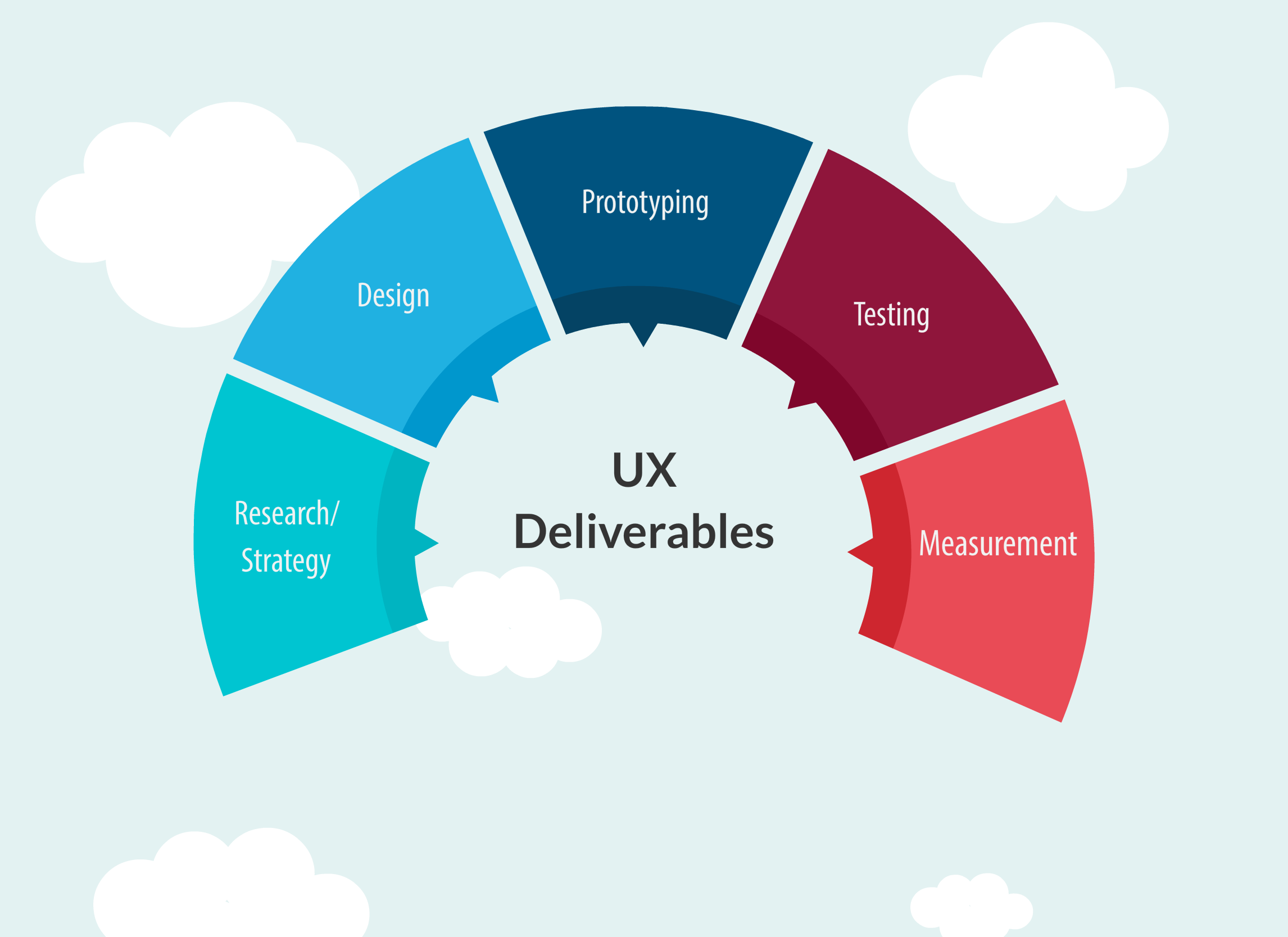
According to one of the leading computer user interface and user experience consulting firm, Nielsen Norman Group, UX “encompasses all aspects of the end-user interaction with the company, its services, and its products”.
A good UX is always recognized by its ease of use and elegance. It presents a seamless combination of marketing, engineering, as well as elements of industrial, graphic and interface design. A good software development company with a product DNA can make your UX phenomenal, making your product standout.
As per the Enterprise UX Industry Report 2017-2018, major enterprise UX challenges include improving consistency (59%), testing designs with end-users (53%), clarifying requirements (46%), and collaborating between teams (44%), among others.
In simple words, the UX process can be thought of a multi-layer cake, which is nothing but a sequence of steps needed to build a solid user experience.
Research/Strategy: This is a base layer which acts as a supporting layer for all the subsequent layers. The foundation layer deals with the formulation of user needs and site objectives for a particular project.
This is important because keeping the desires of your prospect in mind would eventually going to help you and your client to figure out the best possible solution into trackable and measurable goals which will certainly be a rewarding thing for both parties. You can define the complete research process in two categories i.e. primary research and secondary research.
|
Primary Research |
Secondary Research |
|
Analytics/Proprietary Data |
Search Data |
|
User/Usability Testing |
Third Party Studies |
|
Focus Groups |
Paid Reports |
|
On-site Observations/Session Recordings |
Industry and Competitive Audits |
|
Online Email Surveys |
Social Audits |
Design: Once enough secondary and primary information is collected, developers can then put their focus around product designing which helps them to structure their content and think about the customer journey” or a number of steps the end user will take while using that product.
This could be done using “wireframing”, which is a visual representation of the product, including navigation, content, and ways for interactions. These techniques help designers to enhance customer self-efficiency and provide the greater effectiveness of page navigation.
Moreover, in order to determine the usability of a product which is certainly an important part of any design process, cognitive walkthroughs could be one of the best options for you.
Cognitive walkthrough allows a system or a product to be examined for usability from a user’s perspective and generate a quick feedback by asking different set of questions to user for effective design process and decision making.
Prototyping: In the prototyping phase, designers create a draft version of the product or site. The various aspects of prototyping may include experimenting with designs, repairing errors and inconsistencies, developing data to improve upon original ideas, demonstrating products to management, checking to see if the products are usable and functional.
Some of the best prototyping tools for web and mobile design includes InVision (mobile & web), Justinmind (mobile & web), UXPin (mobile & web), Marvel (mobile & web), Origami (mobile & web), and Pixate (mobile only), among others.
Testing: Testing UX can be as simple as observing product/customer’s interactions or as complex as introducing different versions of the product in the market to check which version of the product attracts the customer most.
To test their product, developers may conduct surveys by providing questionnaires or even do further primary interviews with their respective clients in order to identify several loopholes or confusion in the project. Besides, several analytics tools like Google analytics can be an effective solution to know user journeys and their are of interests.
Furthermore, GOMS (Goals, Operators, Methods, and Selection) is a family of predictive models of human performance that can be used to enhance or improve the human machine interaction through elimination of avoidable user actions. Adding more, a heuristic evaluation can be very helpful to detect usability problems in the UI design.
Measurement: It’s important to note that UX is a continuous process which does not end with the official launch of any product. It should continue throughout the complete lifecycle of a product.
As a part of measurement phase, developers must continually test product performance and check if they are meeting the desired set of standards set by their customers. This might include things such as how often customers are recommending your products to other companies and how they use the product itself.
Conclusion: Ultimately, the only goal of UX is to allow organizations to make products that are useful and provides complete experience. We all know that estimating big tech projects is a difficult task and thus the focus with agile is on just in optimizing throughput, problem-solving and decision making.
With so many unknowns this is a much more realistic and rational approach than trying to plan and estimate everything up front. Unfortunately, while this organizing principle works fine for developers, this can be a problematic thing for designers who need to manage things as a part of a coherent system, rather than a series of functional chunks.
One of the ways to tackle this problem is to give in to the inherent uncertainty and allow the design to emerge over time or work with experienced software outsourcing companies having a product thinking . However, this can ultimately place you in a situation where you have a high design debt and hoping to sort all the disparate pieces together when the project ends.
Sometimes, this is possible, but in most of the cases, the situation becomes worse in favor of more functionality. This is one of the key reasons why so many established tech enterprises struggle to produce a holistic user experience and end up creating a disjointed UI instead.
With UX spreading across enterprises, development teams worldwide are experiencing the growing pains of scaling design culture and processes. Nevertheless, they are quickly updating themselves with new collaborative processes and toolkits including several agile methods and latest design system. In short, UX could be one of the important assets a company can offer.
Also Read: Color theory in web design
