Hey, we are looking rate at which the IT sector has developed in recent years has made a remarkable impression across industry verticals, making it possible for businesses to achieve more with the resources and infrastructure available at their disposal. Of all these tech advancements and cutting-edge solutions, cloud computing has been a real game changer. The ability to employ these services swiftly and with minimal management has remained its biggest drawcard.
Cloud computing is an umbrella term that comprises a collection of different services aimed at creating cost-effective solutions for optimizing IT functionality and capacity. These different types of cloud computing services are fundamentally different deployment models, each with a unique
set of features and control over the information. Each of these cloud computing services comes with its own set of advantages, and new features fit to suit the specific requirements of different organizations, businesses, or enterprises. The versatility offered by the different types of services is what makes cloud computing efficient and viable IT solution for a broad cross-section of users, as it gives them the freedom to determine how, where, when, and to what extent they want to adopt this technology.
Types of Cloud Models
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
This the most commonly used cloud computing service model owing to its structural support that includes virtual servers, operating systems, network, and data storage drives. The IaaS model caters to the businesses’ basic need for scalability, flexibility, and reliability vis-a-vis the cloud, as well as obliterates the need for maintaining hardware in the office space. It is a completely outsourced service that operates on a pay-for-use model and is available in private, public, and hybrid infrastructure formats.
Given the specialization and scale involved, IaaS can be a profitable model for businesses using it as well as vendors providing it. Using IaaS inevitably brings in an element of complexity, but it also gives the user unparalleled flexibility. The IaaS model is, therefore, best suited for small and medium organizations that need cost-effective yet easily scalable IT solutions capable of supporting business growth.

2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
This cloud computing model deploys software and infrastructure framework offered by the cloud service providers with room for businesses to develop and run applications of their own as well. PaaS clouds are developed within IaaS clouds in many cases by specialists with a view of scaling the process of application deployment, making the users’ expenses highly predictable. With PaaS, web applications can be developed with ease and in a time efficient manner, and the cloud service carries the requisite robustness and flexibility to support the process.
One of the key benefits of this service is that you can initiate an application with next to no monetary investment. All you have to deal with is essential development (or port, in case of an existing application). PaaS also facilitates scalability by nature of its design, making it suitable for organizations that want to maintain a lean operations staff. It is ideal for business setups that revolve around either leveraging existing data sources or involve projects that require inputs from multiple developers.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is relatively knowledgeable service, and the use of the term predated cloud computing. In this service model, applications leverage the cloud for software architecture, thus, cutting back significantly on burdens of operations, support, and maintenance. This is made possible by running applications on vendor computer as opposed to that of the user. This service makes software available to various users over the internet who, then pay for it either by signing up for a subscription or via a pay-per-use model.
Since SaaS is managed from centralized locations, organizations deploying this service are not concerned with its maintenance. It can prove to be a valuable tool for CRM, as well as apps that require extensive mobile or web access. SaaS is also the ideal cloud computing service for short-term projects.
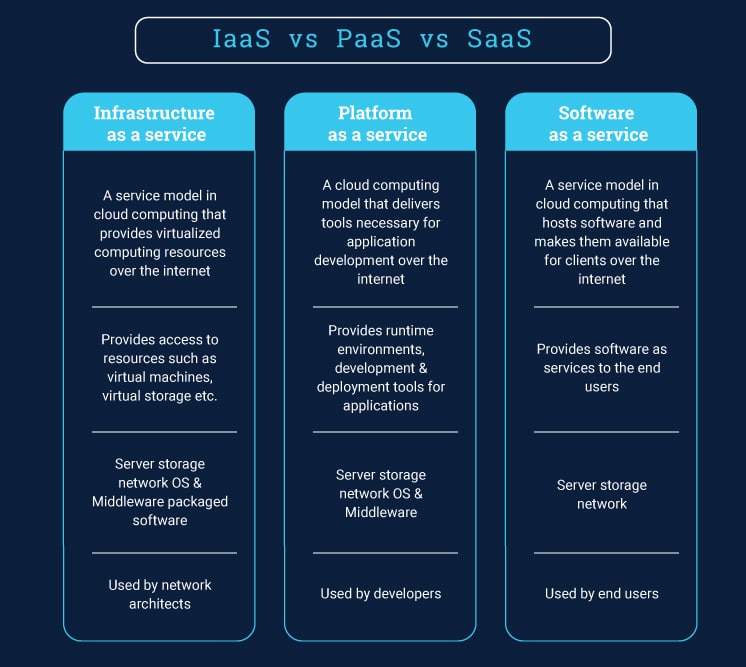
Difference Between Iaas, PaaS, and SaaS
The three primary cloud computing services have their distinct features, usability, and scope.
IaaS uses third-party applications to provide computing resources, storage, servers, and so on to makes these available for the customers’ utilization. Customers can further use IaaS to build their own PaaS or SaaS services.
The PaaS model relies on a third-party vendor to provide services and platform on which a customer can build their application. All of this infrastructure and the necessary tools are made available to the customers via the internet.
The SaaS model uses a third-party provider as a host for multiple applications that are made available to the customers over the internet. It works efficiently as a pay-for-use model.
It is not just the core characteristics that set these cloud computing models apart from one another. These are equally distinct at the service level as well. The essential service-level differences become apparent when these models are compared on critical requirements of any server – application, runtime, framework, data, server, operating system, network stack, and disk.
In the case of Infrastructure as a Service, parameters such as disk, server, and network stack become irrelevant as handling the hardware is no longer the customers’ concern. With Platform as a Service, in addition to disk, server, and network stack, elements such as framework, operating system, and runtime also become immaterial to the customer. Here, the only aspects end users need to focus on is data and application. With the deployment of the Software as a Service method, the customers are not concerned with any of the parameters mentioned above. All you’ve got to do is get the code in order and then foot the bill for the services you use.
The Bottom Line
From this analysis, SaaS may be the simplest of the cloud computing services, and it is. However, simple does not always mean suitable. Finding the right fit in cloud computing services goes beyond the merits and features of these models and also depends on the structure and requirements of the organization seeking to deploy them.
Need a partner to help you find the right cloud computing services to fit your needs? Let the team of experts at Cuelogic help you. Our product-focused, software-driven approach has time and again succeeded in finding the right solutions to suit ever-changing business needs.
